2018-1 NLP 중간고사 정리
자연어 처리 중간고사가 2주전이다. 여기에다가 공부내용을 정리해둔다. 하지만 벌써 일주일전
Lecture 1
introduction of NLP
항상 그렇듯이 새로운 과목을 듣게 되면 처음에는 이 과목은 얼마나 유용하고 중요하고 기타 등등의 알면 아는척 하기 좋은 내용들이고 몰라도 시험에는 안나오겠지 상관 없으니 PASS! 할까 했지만 그래도 허전하니 link하나 추가
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural-language_processing
추가로 하나만 적으면 NLP가 힘든 이유는 ambiguity 때문이라고 한다.
Lecture 2
Tokenization
Type: text에서 단어의 수 Token: text에서 얼마나 많이 반복되는 지 나타냄 따라서 token의 수는 type의 수보다 항상 크거나 같다
ex) Challenges in natural-language processing frequently involve speech recognition, natural-language understanding, and natural-language generation Token : 13 type: 11 (natural-language이 반복됨)
Token과 type을 비율을 나타내는 값으로 TTR이 있다 (type/token ratio) TTR = type/token
Maximum matching.
내용이 어렵지 않으니 아래 slide로 갈음

Lemmatization
: have to find correct dictionary headword form
Stemming
Reduce terms to their stems in information retrieval e.g., automate(s), automatic, automation all reduced to automat.
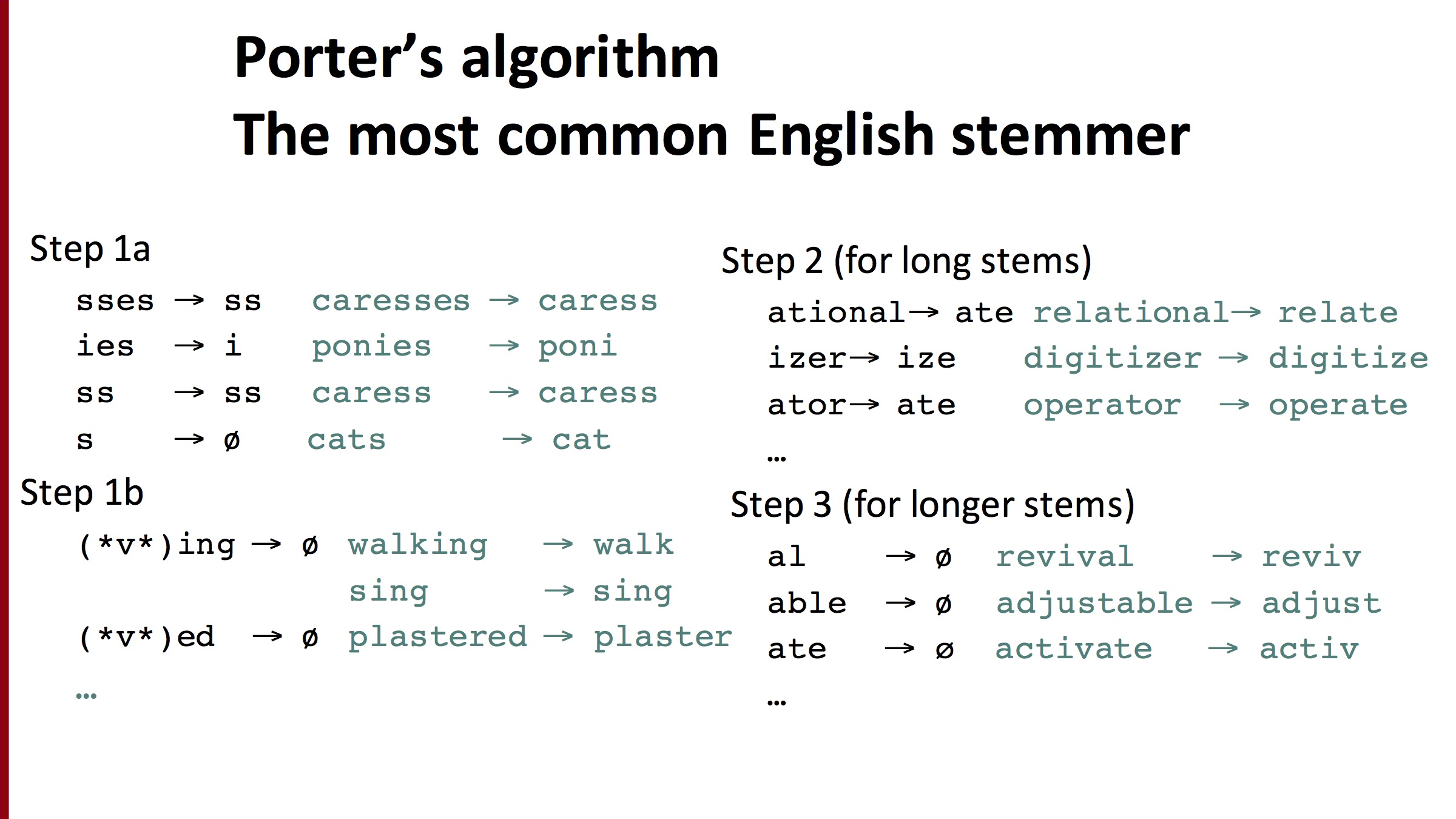
Porter’s algorithm
stemming하는 방법 중 대표적 방법
원문은 https://tartarus.org/martin/PorterStemmer/def.txt 에서 확인가능
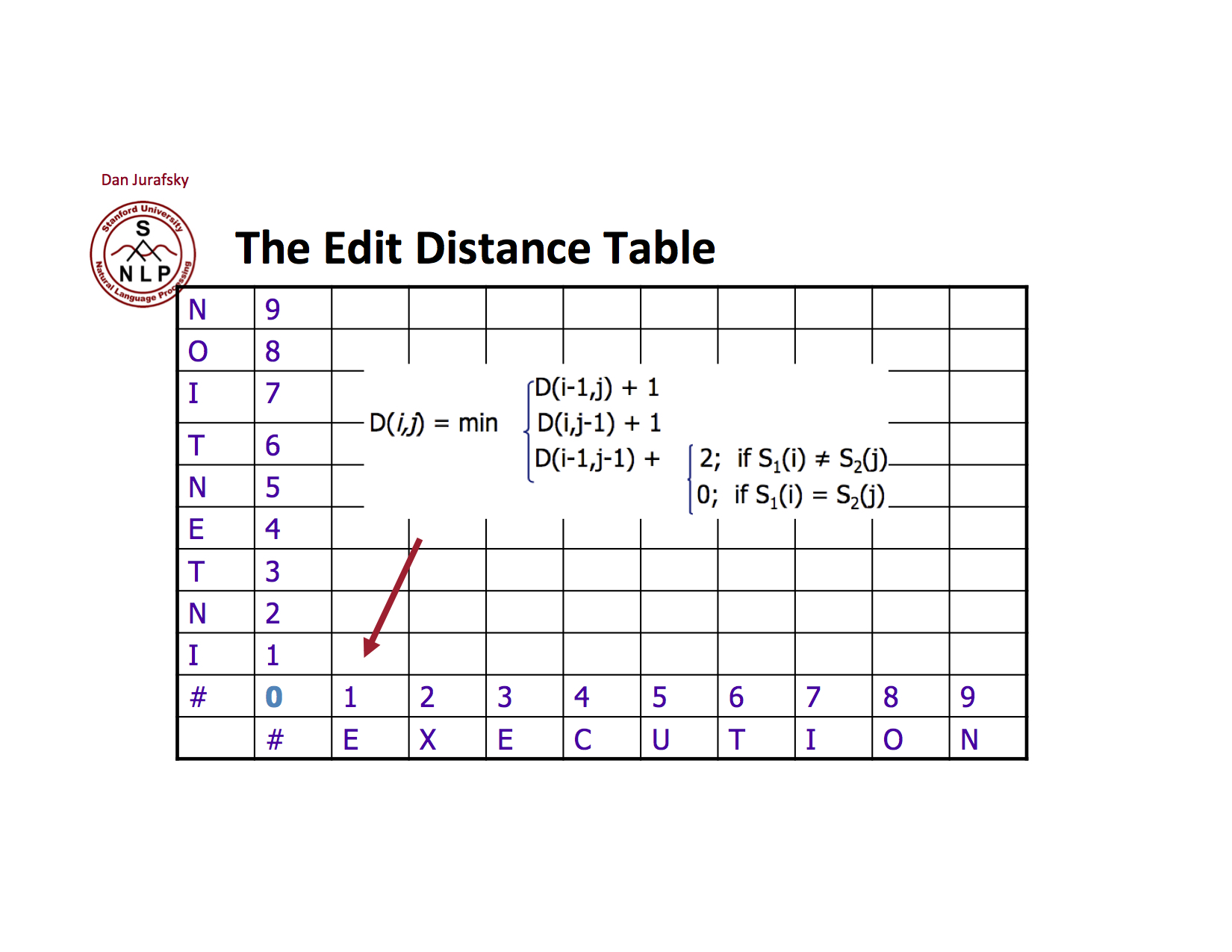
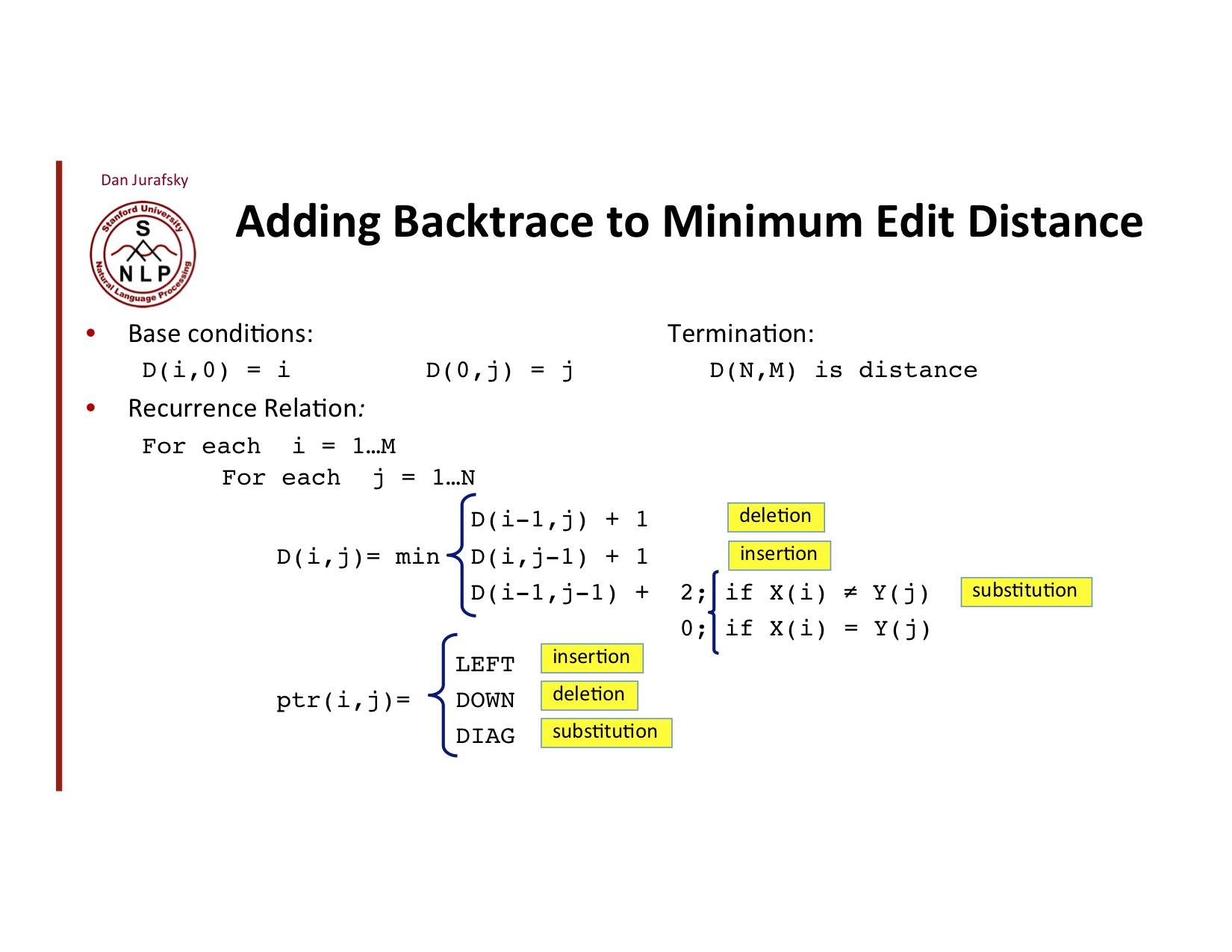
Minimum Edit Distance
Minimum Edit Distance 계산
자세한 algorithm은 아래와 같다

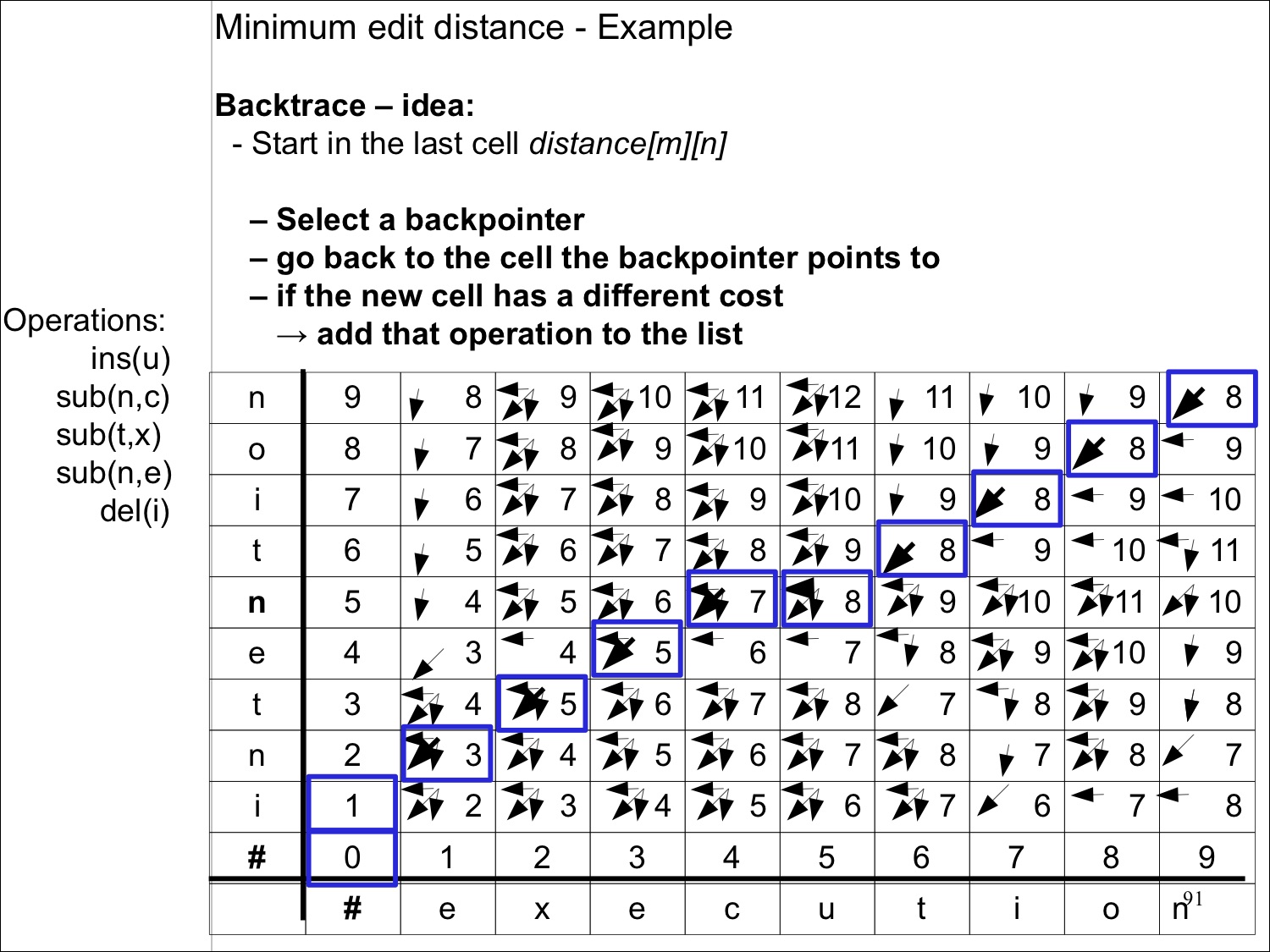
실제 손으로 해볼려면 아래와 같이 table을 만들어 해볼 수 있다 왼쪽과 아래쪽에 쓴다 #은 word가 없는 경우를 나타낸다 각각의 칸은 insert, delete substitution의 경우 cost를 계산하여 가장 작은 값을 적는다 각각의 칸을 채운 후 오른쪽 위 값을 Minimum Edit Distance로 return 한다
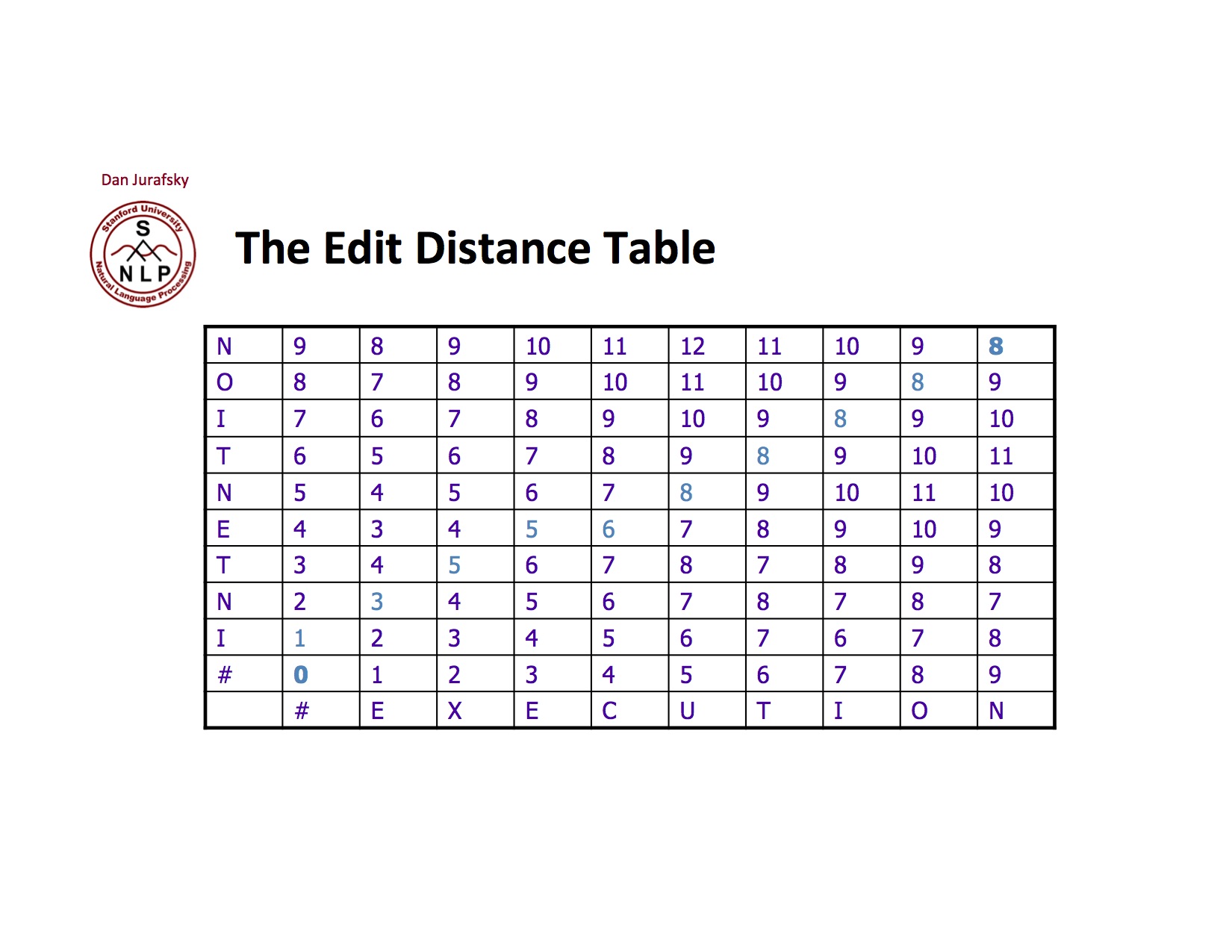
 실제 결과는 아래와 같다 Intention과 Execution의 Minimum Edit Distance은 8임을 알 수 있다
실제 결과는 아래와 같다 Intention과 Execution의 Minimum Edit Distance은 8임을 알 수 있다
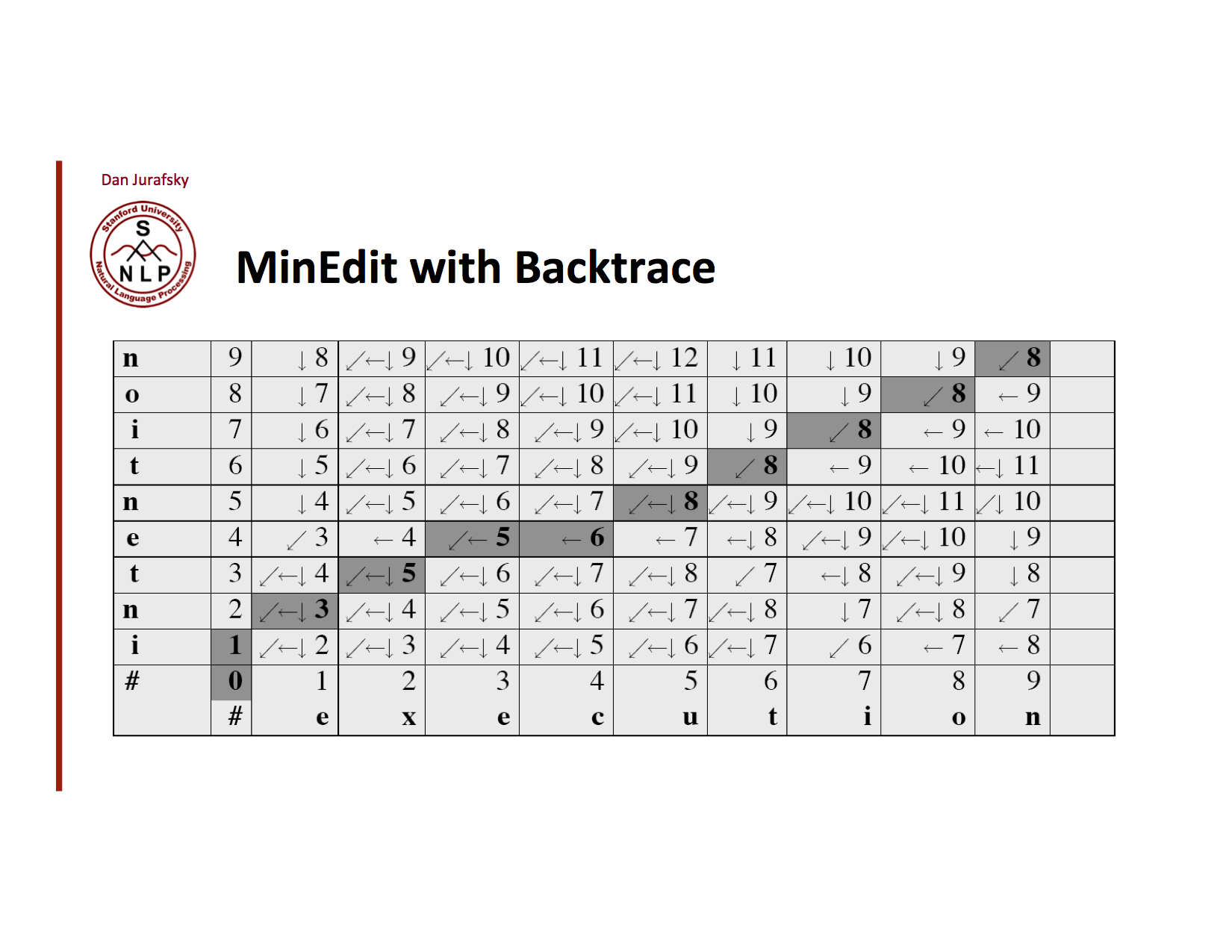
Backtrace
아래로 가는 길은 하나가 아니다.
- 오른쪽 위 부터 0까지 화살표를 따라가면서 기록한다.
- 기록된 화살표의 방향에 따라 insert, delete, substitution을 적는다
- 왼쪽에 세로로 적은 단어에 연산들을 적용하면 끝
Lecture 3
N-Gram
- N-gram is a contiguous sequence of n items from a given sample of text or speech
- An n-gram model models sequences, notably natural languages, using the statistical properties of n-grams. –> which predict the next word from the previous N-1 words
- 2-grams (aka bigrams)
–> (I notice), (notice three), (three guys), (guys standing), (standing on), (on the)
language model
-
A statistical language model is a probability distribution over sequences of words. Given such a sequence, say of length m, it assigns a probability to the whole sequence.
- | → 가 연속되었을 때 가 나올 확률을 나타낸다
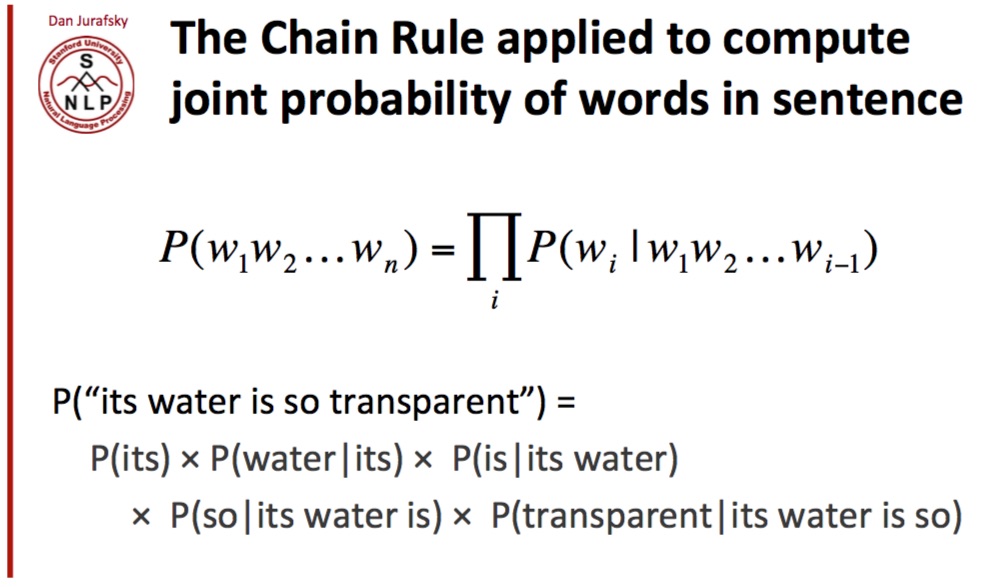
The Chain rule
위 language model을 예측하기 위해서는 아래 식을 계산하면 된다 이론적으로는 말이지
Makov Assumption
이론적으로 언어모델을 계산할 수 있으나 문장이 조금만 길어저도 어디한번 해보시지 계산이 기하급수적으로 늘어난다. 이렇게 되면 실제로 사용하기 힘들어진다. 따라서 약간의(?) 가정을 해서 언어모델을 찾는데 이때 사용한 가정을 Makov Assumption이라 한다 모든 확률을 다 계산하지 말고 N개의 단어가 연속할때 특정단어가 나올 확률을 구하는 것

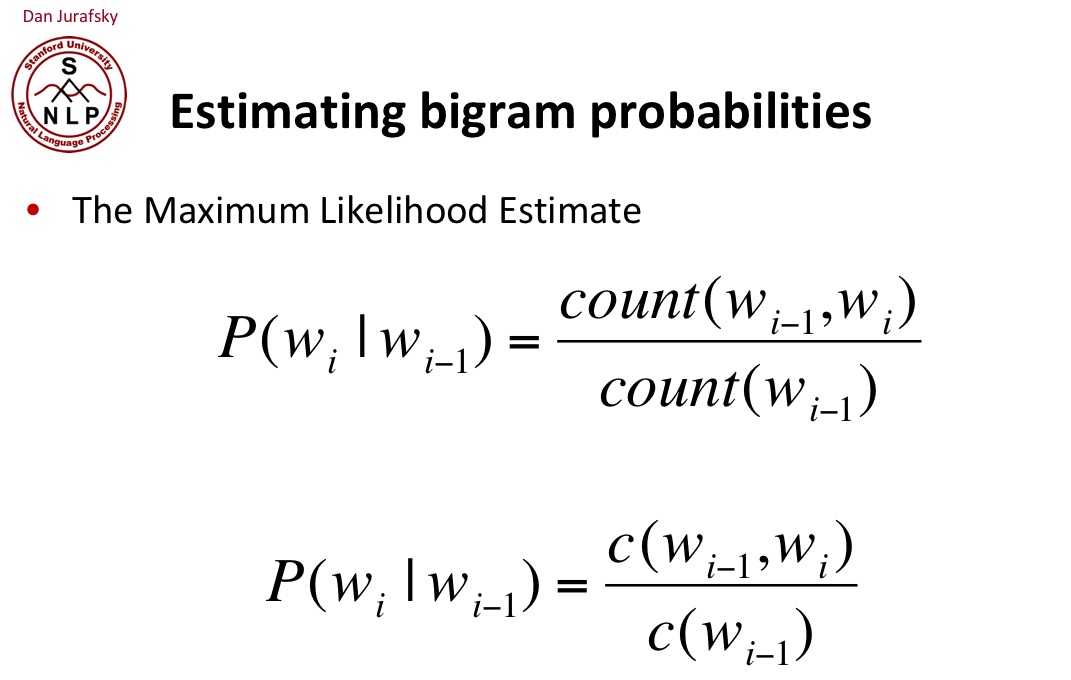
Maximum Likelihood Estimates
어떤 모수가 주어졌을 때, 원하는 값들이 나올 가능도를 최대로 만드는 모수를 선택하는 방법이다.
bigram일때는 아래 공식으로 계산할 수 있다
The Shannon Visualization Method

Evaluation
ML에서 그렇듯 해당 model을 평가하기 위해서는 training set / test set을 나누고 training set을 위해 학습시키고 test set을 가지고 평가한다. 하지만 어떻게?
Extrinsic Evaluation (in vivo evaluation)
- Extrinsic evaluation of word vectors is the evaluation of a set of word vectors generated by an embedding technique on the real task at hand. These tasks are typically elaborate and slow to compute. Typically, optimizing over an underperforming extrinsic evaluation system does not allow us to determine which specific subsystem is at fault and this motivates the need for intrinsic evaluation.
Perplexity
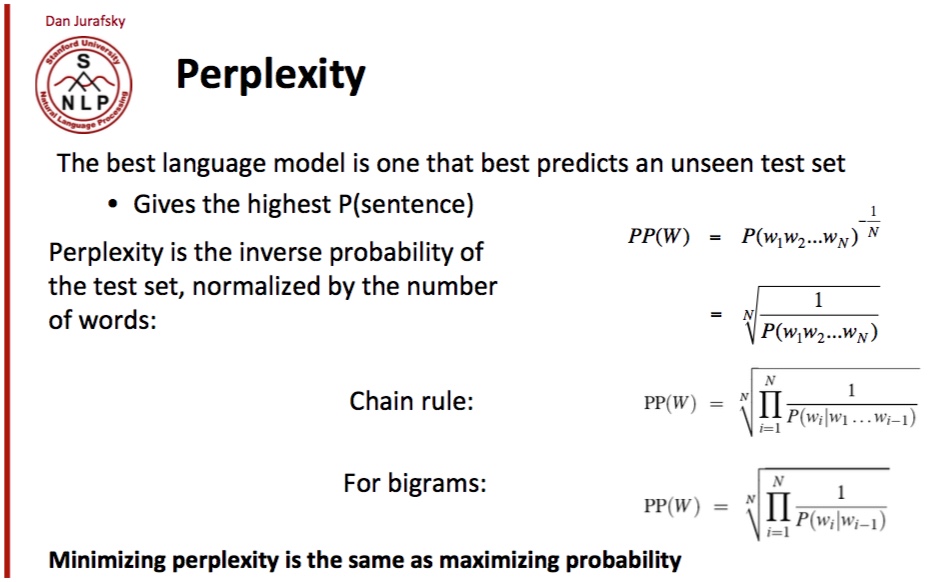
Lecture 4
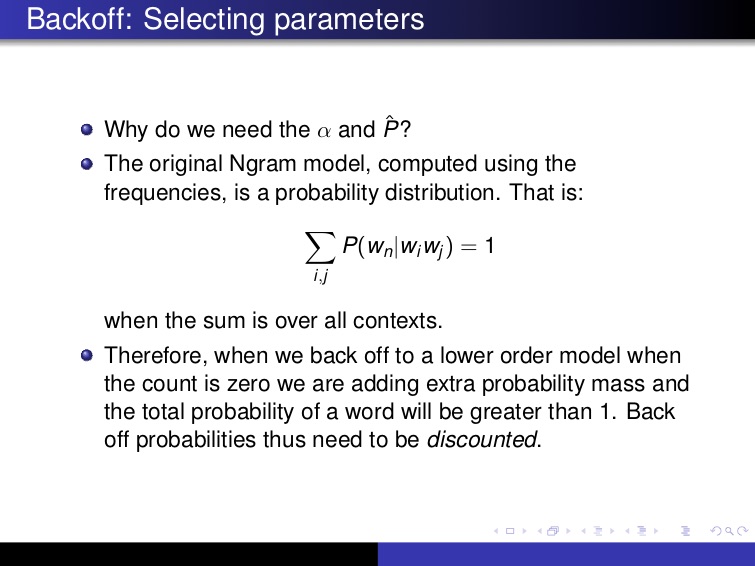
- 우리의 corpus 제한적이니 valid word sequence도 우리의 corpus에 없을 수 있고 결국 zero probability가 나올수 있다. 이를 방지하기 위해 아래의 방법을 사용할 수 있다
그냥 sample을 늘리자
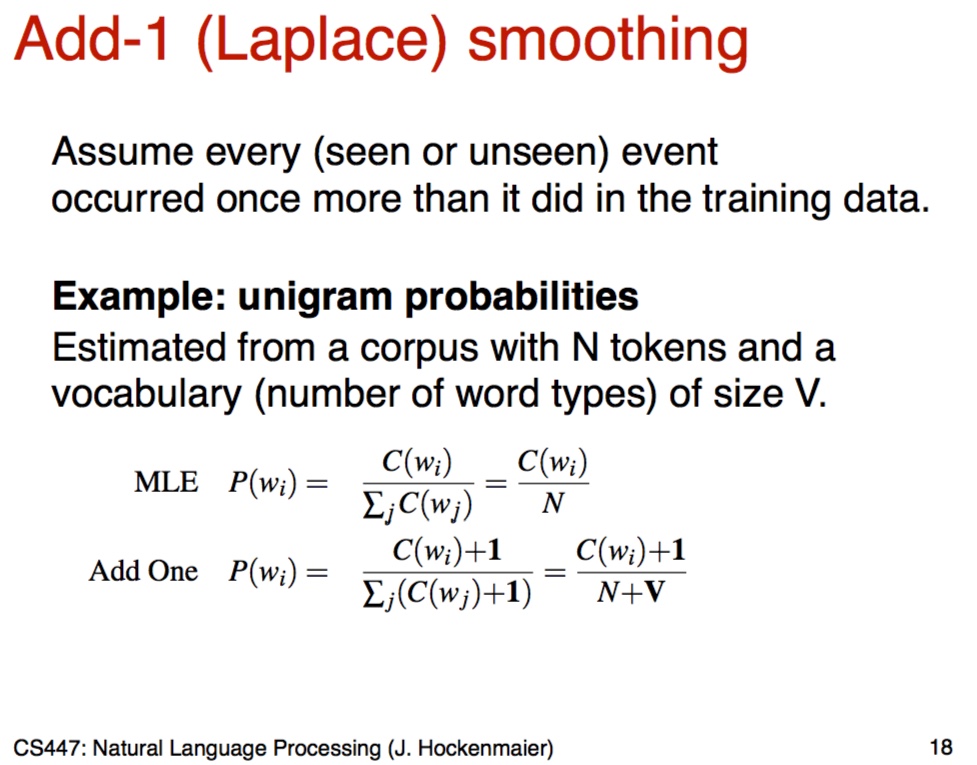
Laplace (Add-1)
- 간단하게 count에 1을 추가해서 0인 가능성을 없게 한다
- 하지만 add-1은 unseen event에 대해 나무 많은 가능성을 부여한다



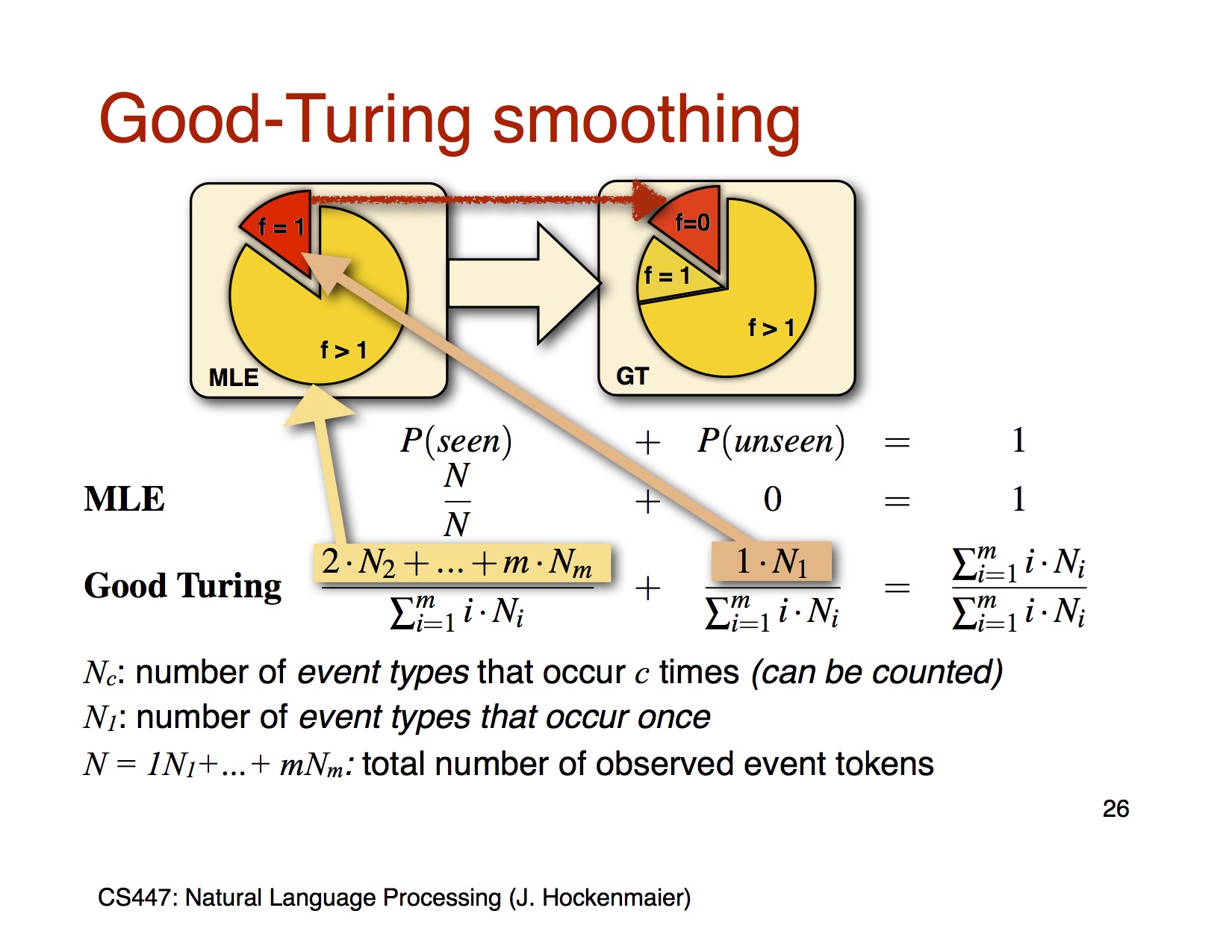
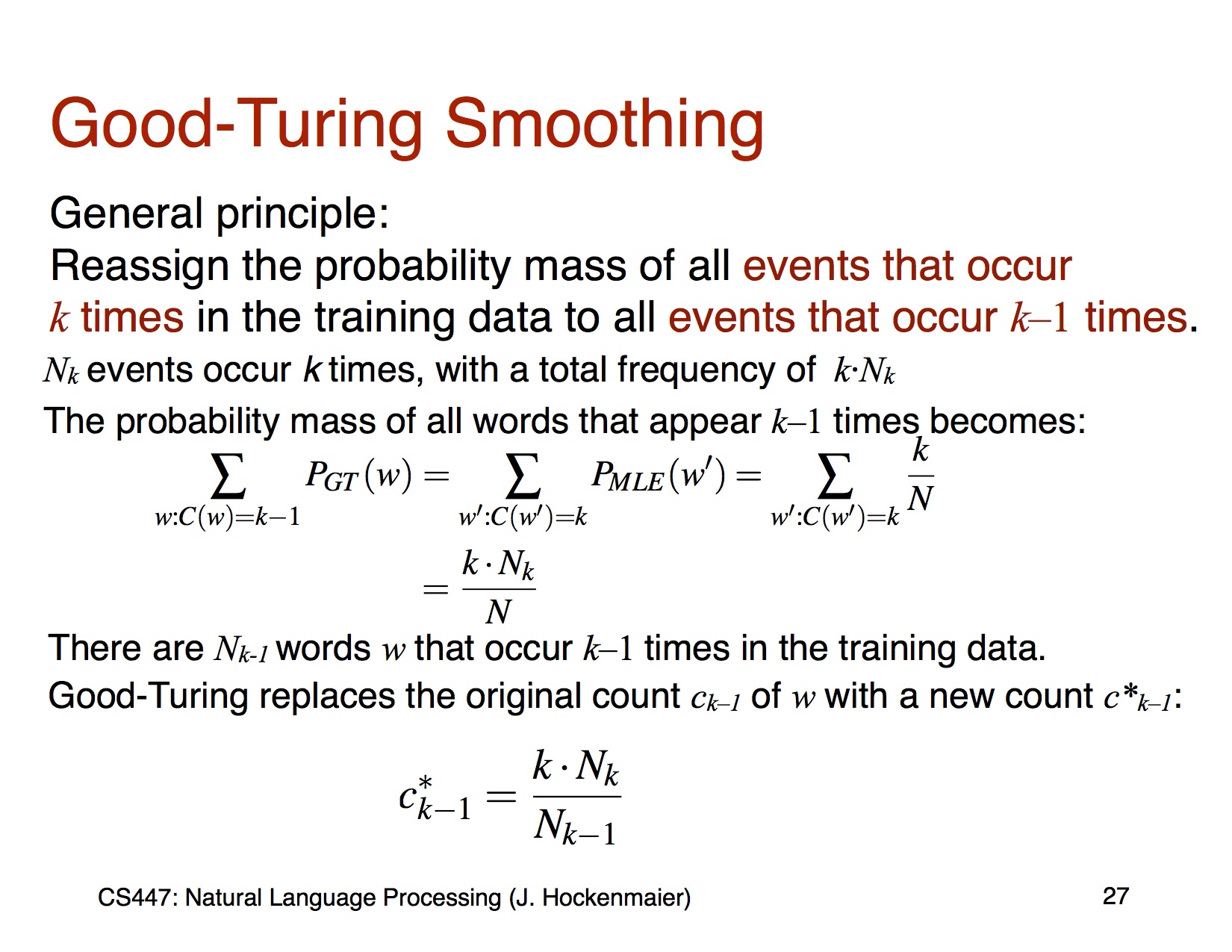
Good-Turning

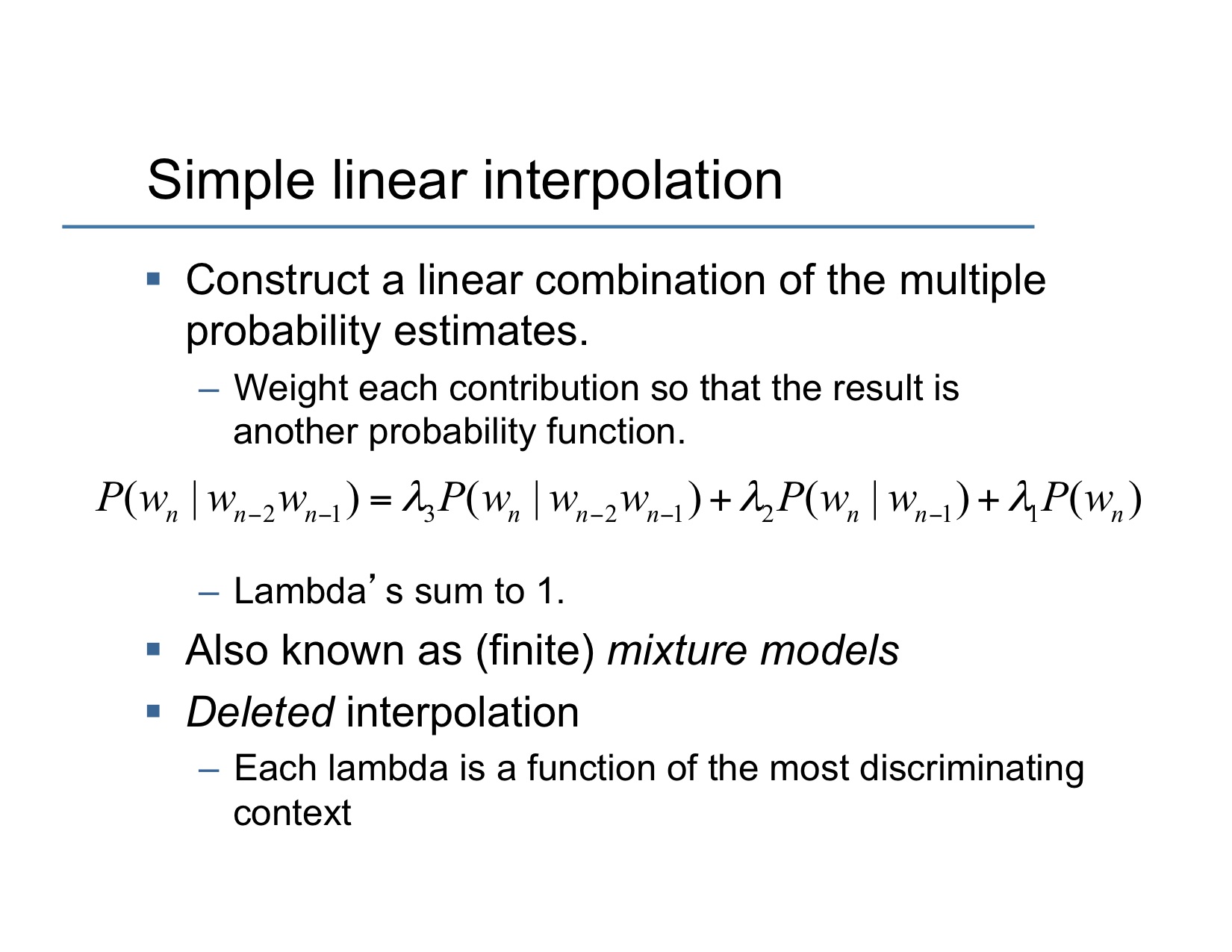
Interpolation
기본 개념은 모르는거 나오면 unigram, bigram, trigram 다 써서 맞추어 보자
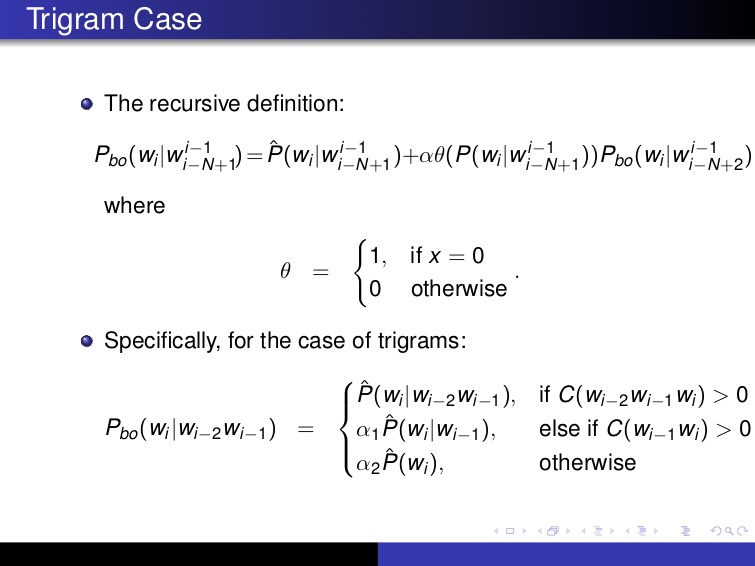
Backoff
일단 N을 모르면 N-1까지 있는 걸로 알아 맞추어 보자




Lecture 5
Part of Speech
위키피디아 정의는 이렇다
In traditional grammar, a part of speech (abbreviated form: PoS or POS) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) which have similar grammatical properties.
그냥 품사라고 생각해도 될듯
Open Close words
Word classes may be classified as open or closed: open classes (like nouns, verbs and adjectives) acquire new members constantly, while closed classes (such as pronouns and conjunctions) acquire new members infrequently, if at all.
- open class : 추가가 가능한 품사들 예를 들어 명사나 동사는 추가되는 경우가 많다
- close class : 추가가 잘 안되는 품사들 (전치사, 관사 등)
추가되면 영어 문법책이 더 두꺼워 지겠지 ㅜㅜ
Part of speech tagging
In corpus linguistics, part-of-speech tagging (POS tagging or PoS tagging or POST), also called grammatical tagging or word-category disambiguation, is the process of marking up a word in a text (corpus) as corresponding to a particular part of speech
좀더 쉬운 정의는 아래 slide 보면 될 듯

HMM Tagging
HMM
내부 상태를 모르는 상태에서 외부로 보여지는 모습만 가지고 내부 상태가 뭔지 알아내는 방법
- 전이 확률
은닉 상태 공간은 범주 분포로 모델링 될 수 있는 N개의 가능한 상태들 중 하나로 구성되어 있다고 가정된다. 각각의 시간 t에서 은닉 변수는 총 N개의 가능한 상태들을 가질 수 있고, 시간 t+1에는 은닉 변수가 N개의 가능한 상태로 전이할 확률이 존재한다.
→ 내부 상태간 전이하는 확률
- 출력 확률
각 N개의 가능한 상태들에 대하여 특정 시간에서의 은닉 변수들이 주어졌을 때 관측 변수들의 분포를 제어하는 출력 확률들의 집합이 존재한다
→ 각 상태에서 관측값들이 출력되는 확률
HMM은 3개의 문제를 해결하는 것으로 볼 수도 있는데 각각은 아래와 같다
- Likelihood 문제 → forward algorithm으로 해결
- Decoding 문제 → 관찰값이 있을 때 내부 상태가 어떤 식이였는지 찾는 방법 : Viterbi algorithm 으로 해결
- learning 문제 → Baum-Welch algorithm으로 해결
하나하나 자세히 보고 싶지만 시험이 코 앞이라
핑계가 좋다일단 수업시간에 다룬 Viterbi algorithm만 정리한다. 나중에 시험 끝나고 HMM은 따로 정리해야 할 듯Viterbi algorithm
Evaluation
cross-validation
dataset을 어려개로 나누고 나누어진 dataset을 training/testing dataset으로 바꾸어가면서 검증 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross-validation_(statistics)
참고자료
- https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs124/
- http://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/2.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
- https://courses.engr.illinois.edu/cs447/fa2017/Slides/Lecture04.pdf
- http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs4740/2014sp/lectures/smoothing+backoff.pdf
- http://l2r.cs.uiuc.edu/~danr/Teaching/CS546-09/Lectures/Lec5-Stat-09-ext.pdf
- http://verbs.colorado.edu/~xuen/teaching/ling5200/ppts/pos-tagging1.pdf
- http://stp.lingfil.uu.se/~evelina/uv/uv14/pst1/F5/editdistance.pdf